Are you intrigued by the world of cryptocurrency? Understanding blockchain technology is key to unlocking its potential. This article dives deep into the importance of blockchain in the cryptocurrency landscape. We’ll explore how this groundbreaking technology ensures security, transparency, and decentralization, fundamentally changing the way we think about digital assets and financial transactions. Prepare to learn why blockchain is not just a buzzword, but the very foundation upon which the future of cryptocurrency is built.
What is Blockchain Technology?
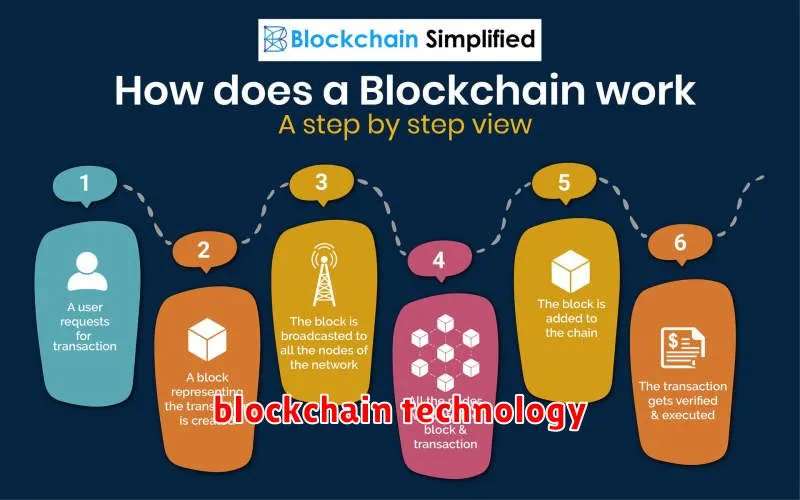
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized, distributed, and public digital ledger that records and verifies transactions across many computers. This means no single entity controls it, making it highly secure and transparent.
Imagine a digital spreadsheet replicated across numerous computers. Every time a new transaction occurs (like sending cryptocurrency), it’s added as a “block” to this spreadsheet. This block is then verified by multiple computers in the network (a process called mining) before being added to the chain. This verification ensures the integrity of the data.
The decentralized nature is crucial. Because the ledger isn’t stored in one place, it’s incredibly resistant to hacking and censorship. If one computer is compromised, the others maintain the integrity of the blockchain. This transparency allows anyone to view the transactions (although user identities are often pseudonymous).
Cryptographic hashing plays a significant role. Each block is linked to the previous one using cryptographic hashes, creating a secure and tamper-proof chain. Any attempt to alter past transactions would be immediately detectable.
In short, blockchain technology provides a secure, transparent, and auditable way to record and manage information, forming the foundation for cryptocurrencies and many other innovative applications.
How Blockchain Ensures Security in Crypto
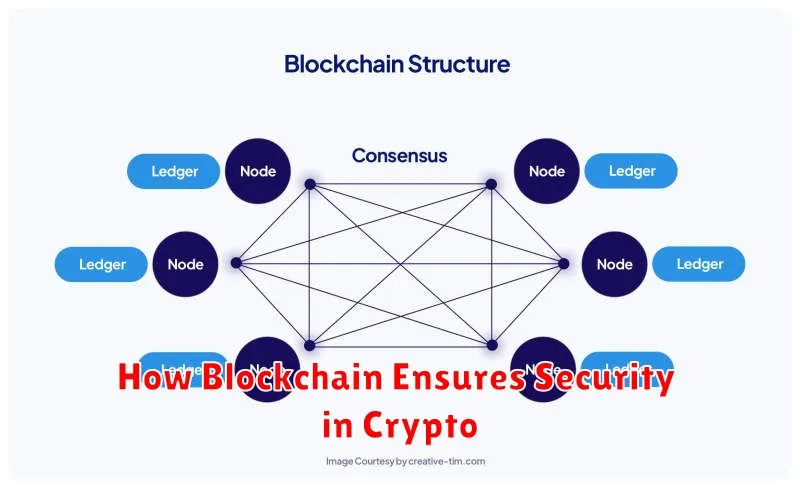
Blockchain technology underpins the security of cryptocurrencies through several key mechanisms. The most fundamental is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional databases controlled by a single entity, a blockchain is distributed across a vast network of computers (nodes). This makes it incredibly difficult for any single actor to manipulate or compromise the data.
Immutability is another critical aspect. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This is achieved through cryptographic hashing, where each block is linked to the previous one using a unique cryptographic hash. Any attempt to change a previous block would alter its hash, breaking the chain and rendering it invalid. This provides a high level of data integrity.
The consensus mechanisms employed by various blockchains, such as Proof-of-Work (PoW) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS), further enhance security. These mechanisms ensure that new blocks are added to the chain only after being verified by a majority of the network participants. This prevents malicious actors from adding fraudulent transactions or altering existing ones.
Furthermore, cryptographic keys provide individual users with control over their cryptocurrency. These keys, essentially long strings of characters, are used to authorize transactions, ensuring that only the rightful owner can spend their funds. The use of public and private keys creates a secure system for transferring ownership.
In summary, the combination of decentralization, immutability, consensus mechanisms, and cryptographic keys makes blockchain technology a highly secure foundation for cryptocurrencies, protecting against fraud, theft, and unauthorized access.
Decentralization: The Core of Blockchain

At its heart, blockchain technology is all about decentralization. Unlike traditional systems that rely on a central authority (like a bank or government), blockchain distributes the power across a network of many computers.
This distributed ledger technology means no single entity controls the data. Every transaction is verified and added to the blockchain by multiple participants, ensuring transparency and security.
This decentralized nature is what makes blockchain so resistant to censorship and single points of failure. If one node in the network goes down, the rest continue to function, maintaining the integrity of the system.
This fundamental principle of decentralization is crucial to the security and trust inherent in cryptocurrencies, eliminating the need for intermediaries and empowering users with greater control over their assets.
The decentralized nature of blockchain also fosters trustlessness, as participants don’t need to rely on the trustworthiness of a central authority. Transactions are verified through cryptographic methods and consensus mechanisms, ensuring data integrity and preventing fraud.
The Role of Blockchain in Transactions
Blockchain technology plays a critical role in cryptocurrency transactions by providing a secure and transparent record of all transactions. This is achieved through a decentralized, distributed ledger that is replicated across a network of computers.
Each transaction is grouped into a “block” which is then added to the existing chain of blocks, hence the name “blockchain”. This creates a chronological and immutable history, making it virtually impossible to alter or delete past transactions.
The decentralized nature of the blockchain eliminates the need for a central authority, such as a bank, to verify and process transactions. Instead, the network of computers collectively verifies each transaction using cryptographic techniques. This process ensures data integrity and prevents fraud.
Furthermore, the use of cryptography secures individual transactions, guaranteeing authenticity and preventing unauthorized access. This enhanced security is a key factor contributing to the trust and reliability of cryptocurrency transactions.
In summary, blockchain’s role in cryptocurrency transactions is fundamental. It provides the infrastructure for secure, transparent, and efficient processing of transactions, laying the foundation for the entire cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain
While blockchain technology is famously associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, its potential extends far beyond digital currencies. Its decentralized and secure nature makes it ideal for a variety of real-world applications.
One key area is supply chain management. Blockchain can track products from origin to consumer, enhancing transparency and preventing counterfeiting. This is particularly beneficial for industries with complex supply chains, like pharmaceuticals and food.
Healthcare is another promising sector. Blockchain can securely store and manage sensitive patient data, improving data privacy and interoperability between healthcare providers. It can also streamline the process of managing medical records and insurance claims.
Voting systems could be revolutionized by blockchain. Its immutability ensures the integrity of votes, making elections more secure and transparent. This could help build greater trust in democratic processes.
Digital identity management is also being explored. Blockchain can create secure and verifiable digital identities, reducing identity theft and fraud. This is crucial in a world increasingly reliant on online interactions.
Furthermore, intellectual property rights management can benefit from blockchain’s secure and transparent nature, allowing creators to easily prove ownership and prevent unauthorized copying.
These are just a few examples of how blockchain technology is transforming various industries. Its decentralized, secure, and transparent nature provides solutions to many long-standing problems, paving the way for a more efficient and trustworthy future.
How Smart Contracts Enhance Blockchain Usability
Smart contracts significantly improve blockchain usability by automating processes and eliminating intermediaries. They are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code.
This automation makes transactions faster and more efficient. Instead of relying on manual approvals and lengthy processes, smart contracts execute automatically when predetermined conditions are met, ensuring speed and reliability.
Furthermore, smart contracts enhance transparency and trust. All transactions and agreements are recorded on the blockchain, providing a permanent and auditable record for all participants. This eliminates the need for trust in a central authority.
The increased security offered by smart contracts is another key advantage. Because the code is immutable and stored on the distributed ledger, tampering or manipulation is nearly impossible. This fosters trust and reduces the risk of fraud.
Usability is further boosted by the ability to create a wide range of applications beyond simple financial transactions. Smart contracts can be used for supply chain management, voting systems, digital identity verification, and much more, expanding the potential of blockchain technology.
In essence, smart contracts bridge the gap between the complex technology of blockchain and its practical application. They make blockchain more accessible and user-friendly, unlocking its potential for a broader range of uses and users.
Future Trends in Blockchain Technology
The future of blockchain technology is brimming with exciting possibilities. Scalability remains a key focus, with solutions like sharding and layer-2 scaling solutions aiming to increase transaction throughput significantly. This will be crucial for wider adoption and handling the increasing demand for blockchain applications.
Interoperability is another significant trend. Different blockchain networks currently operate in silos. The development of cross-chain communication protocols will allow seamless transfer of data and assets between various blockchains, enhancing functionality and efficiency.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) will continue its explosive growth. We can expect to see more sophisticated DeFi applications, improved governance models, and increased integration with other blockchain technologies. Privacy-enhancing technologies, like zero-knowledge proofs, are gaining momentum, addressing concerns about data confidentiality on public blockchains.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and blockchain are poised for a powerful synergy. AI can enhance blockchain security and efficiency through tasks like fraud detection and smart contract optimization. Meanwhile, blockchain can provide the secure and transparent infrastructure for AI applications, addressing issues of data ownership and bias.
Finally, regulatory clarity will be vital for blockchain’s mainstream adoption. As governments worldwide grapple with the implications of this disruptive technology, clearer regulatory frameworks will unlock its full potential and foster innovation.